


Yes! It is only a low trading commission. But the service is always high level and satisfactory
We understand that every trader is unique. That's why we offer three distinct account types tailored to suit your trading style and preferences
We love connecting with our clients to hear about their experiences and how we can improve.
With a sleek and carefully designed UI, buying, selling, analysing, and managing your portfolio, everything's just a click away


At Rifa FX, we believe that the best trader is an educated one. We analyse and explain the price movements of the global markets, giving traders all the in-depth knowledge they need to make their next move.
Keep on top of the latest forex news, including updates on popular currencies such as the GBP, USD and EUR, commodities markets and more from our very own FX market specialists.
Rifa FX's super-fast flagship trading platform with elegant UI, Inbuild strategies, streaming market data, advanced charts. Experience the way of trading.


Place Target Point &
Stop Loss From Charts

Hundreds of indicators, studies, and tools on a powerful and customisable charting interface. Extensive historical data for forex, crypto, stocks and metals from 20+ exchanges. Nobody else offers as much data as we do.
Unlock the full potential of our product with our amazing features and top-notch.

Trusted Forex Broker
Enjoy Tech,Enjoy Trading

Partner in Financial Growth
Enjoy Tech,Enjoy Trading

Empowering Your Financial Future
Enjoy Tech,Enjoy Trading

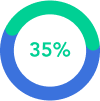
Achieve More with Forex Trading
Enjoy Tech,Enjoy Trading

We pride ourselves on being a brokerage that prioritizes the success and satisfaction of our traders
Mobile trading refers to trading in the stock market, using a smartphone.
A online trading app is a mobile application on which you can buy and sell stocks and invest in other assets online.

TradingView gives you access to highly interactive, responsive and mobile-friendly charts optimized for touch devices.

An application programming interface (API) establishes an online connection between a data provider and an end-user.
You'll find the key to unlocking the doors of trading success.
Hey there pro traders, check out these articles with tips to take your trading game to the next level!